General Conformity
General conformity is a process required by the Clean Air Act (CAA), which establishes the framework for improving air quality to protect public health and the environment. On November 30, 1993, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) promulgated General conformity Regulations which apply to all federal actions other than the highways and mass transit. The regulations were revised on April 5, 2010.
These regulations were put in place to prevent air quality impacts of Federal actions from causing or contributing to a violation of the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) or interfering with the purpose of a State Implementation Plan (SIP), Tribal Implementation Plans (TIP) or Federal Implementation Plan ( FIP) in a nonattainment or maintenance areas.
The implementation of the existing General Conformity Regulations process falls into three phases:
- Applicability Analysis
- Conformity Determination
- Review Process
General Conformity does not apply to actions:
- Affecting cars and buses (actions subject to transportation conformity);
- Causing a small amount of emissions (de minimis levels);
- That are presumed to conform; and
- Specifically identified in the regulations as exempt
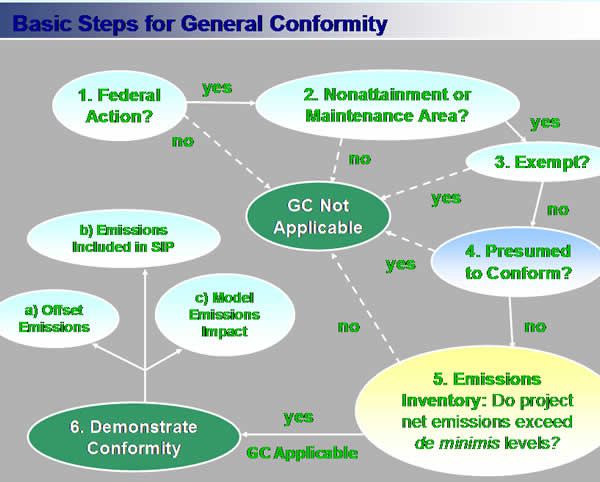
(Image credit: //www.epa.gov/oar/genconform/training/01_mod_1_Sec_1-1.html)
NB: Anchorage has completed its CO 20-year limited maintenance period. Hence, the requirements for a general conformity determination/applicability analysis as provided in CAA section 176(c) and 40 CFR part 93 no longer apply to any federally funded projects/actions within Anchorage.
However, since the PM10 maintenance period for Eagle River and Juneau is still on until 2033, general conformity determination/applicability analysis is required for federally funded projects/actions in Eagle River and Juneau maintenance areas until 2033. Also, despite the completion of the CO 20-year maintenance period in Fairbanks, general conformity determination/applicability is still required for federally funded projects/actions in the Fairbanks PM2.5 nonattainment area.

 Indicates an external site.
Indicates an external site.