Fish Waste Disposal
Improper disposal of fish waste from sport fishing, personal use fishing, and commercial fisheries poses a potential risk to the environment and public health and safety. The ADEC Solid Waste Program only regulates the land disposal of fish waste from commercial operations. However, it is important to understand the best management practices for disposing fish waste to reduce nuisances and animal attraction.
Personal Use and Sport Fish Waste
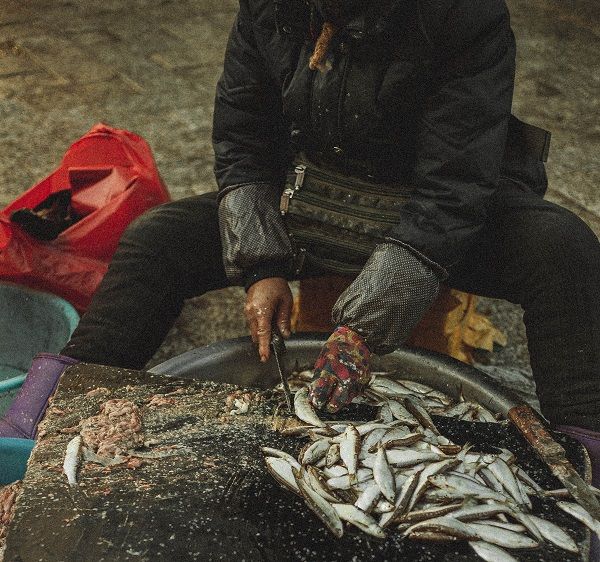

Even for sport and personal use fishing, disposing of fish waste on public or private land is illegal and can result in fines. The Alaska Department of Fish and Game recommends that you clean fish riverside or in port, chop fish carcasses into numerous pieces, and throw them into deep or fast-moving water or use a provided fish grinder. Anglers who remove fish from the fishing site and fillet or process them must also dispose of fish waste in a safe manner. http://www.adfg.alaska.gov/index.cfm?adfg=fishregulations.sfbears&_ga=2.96255068.1516895671.1524601729-768014924.1524601729
Fish waste should be taken directly to a permitted landfill that will accept it.
- The Central Peninsula Landfill in Soldotna accepts fish waste free of charge during the fishing season.
- Anchorage Regional Landfill, the Central Transfer Station, and the Girdwood Transfer Station accept residential fish waste.
- Matanuska-Susitna Borough takes bagged residential fish waste at the Palmer Central Landfill and the Big Lake, Butte, and Sutton transfer stations.
If you have local trash pickup, freeze the fish waste to eliminate odors and then put it out of the morning of your trash pickup day. Do not place waste out the night before or put it in commercial dumpsters.
Commercial Fish Waste
ADEC Solid Waste Program allows three methods for managing commercial fish waste on land:

- Landfill Disposal: Commercial fish waste may be disposed in a permitted landfill willing to accept it.
- Land Application: Fish waste may be ground and tilled into agricultural or silvicultural land as fertilizer, provided the waste is processed and treated as prescribed in the solid waste regulations.
- Composting: Fish waste can be composted to create a usable product. Several successful composting projects have been operated in Alaska. The Alaska Sea Grant's guidance Safe and Legal Fish Waste Composting in Alaska discusses proper composting operations. Depending on the volume of waste involved, a composting operation may require a solid waste treatment permit or plan approval.https://seagrant.uaf.edu/bookstore/pubs/ASG-55.html
Commercial fish waste placed on land must be carefully managed to minimize pathogens, odors, animal attraction, and contamination of water resources. Improper management of fish waste can attract wildlife and pose a serious risk to health, safety, and the environment. Contact the ADEC Solid Waste Program to determine if your project requires an authorization.http://dec.alaska.gov/eh/solid-waste/contacts/
Disposal of commercial fish waste in water requires a permit from the ADEC Wastewater Discharge Program. http://dec.alaska.gov/water/wastewater/seafood/
Related Regulations
18 AAC 60.040(b): A person may not dispose of septage, sewage solids, fish waste, animal manure, or animal byproducts or waste on the ground within 100 feet of a well that produces water suitable for drinking.
18 AAC 60.010(e) Land Application of Fish Processing Waste: Subject to 18 AAC 60.040(b), a person who wishes to dispose of organic waste from a commercial slaughterhouse or fish processing waste may apply that waste to agricultural or silvicultural land for soil enhancement purposes if the waste is:
- ground up to less than two inches in diameter;
- treated by a method described in 40 C.F.R. 503.15, revised as of July 1, 1997, adopted by reference, to reduce the number of salmonella spp. or fecal coliform bacteria present to meet the Class A requirements for pathogen reduction at the time of land application;
- incorporated into the soil surface when the waste is applied;
- applied at or below the agronomic rate for nitrogen for any crop or vegetation that will be grown on that land;
- applied in a manner that does not create an odor nuisance or attract animals or other vectors; and
- applied in a manner that ensures that run-off of surface water from the disposal site does not violate the water quality standards in 18 AAC 70.

 Indicates an external site.
Indicates an external site.